VIDEOSMENU
VIDEOSMENUUterine Fibroid
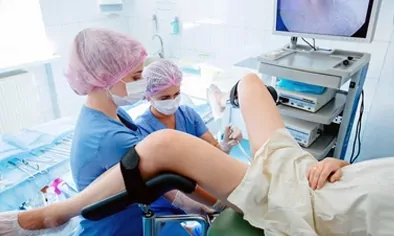
Uterine Fibroid Surgery
Fibroids are tumors arising from the benign smooth muscle cells of the uterus. It is not large enough to cause complaints in most patients and is followed without the need for a biopsy diagnosis.
REVIEWOvarian Cyst
Ovarian Cyst Surgery
Ovarian cyst surgery is an operation in which the cyst in the ovary is removed, the ovary is protected and the cyst is sent for pathological examination.
REVIEWEndometriosis
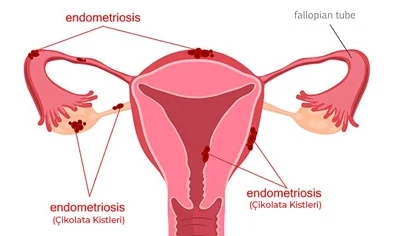
Endometrioma Cyst Surgery
Chocolate cyst is the gland tissue (endometrium) that forms the inner part of the uterus and provides menstruation which is located outside the uterus. Endometriosis is a disease of theories.
REVIEWHysterectomy
Uterus Removal Surgery
Uterine removal surgeries are called hysterectomy in traditional medical literature. It is a surgery to completely remove the uterus from the body.
REVIEW